Dental Plaque on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dental plaque is a

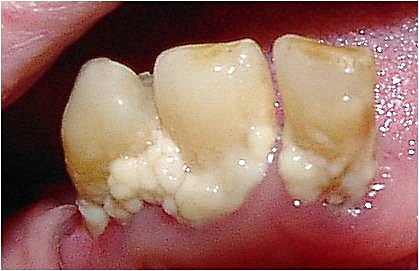 Subgingival biofilm is plaque that is located under the gums. It occurs after the formation of the supragingival biofilm by a downward growth of the bacteria from above the gums to below. This plaque is mostly made up of anaerobic bacteria, meaning that these bacteria will only survive if there is no oxygen. As this plaque attaches in a pocket under the gums, they are not exposed to oxygen in the mouth and will therefore thrive if not removed.
The
Subgingival biofilm is plaque that is located under the gums. It occurs after the formation of the supragingival biofilm by a downward growth of the bacteria from above the gums to below. This plaque is mostly made up of anaerobic bacteria, meaning that these bacteria will only survive if there is no oxygen. As this plaque attaches in a pocket under the gums, they are not exposed to oxygen in the mouth and will therefore thrive if not removed.
The

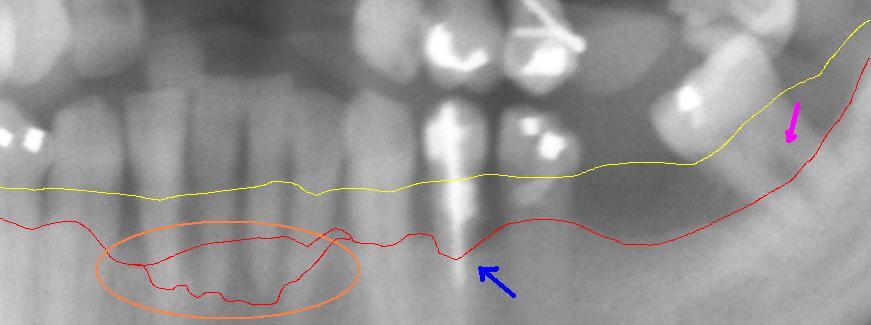 Periodontitis is an infection of the gums which leads to bone destruction around the teeth in the jaw. Periodontitis occurs after gingivitis has been established, but not all individuals who have gingivitis will get periodontitis. Plaque accumulation is vital in the progression of periodontitis as the
Periodontitis is an infection of the gums which leads to bone destruction around the teeth in the jaw. Periodontitis occurs after gingivitis has been established, but not all individuals who have gingivitis will get periodontitis. Plaque accumulation is vital in the progression of periodontitis as the
 Plaque disclosing products, also known as disclosants, make plaque clinically visible. Clean surfaces of the teeth do not absorb the disclosant, only rough surfaces. Plaque disclosing gels can be either completed at home or in the dental clinic. Before using these at home or in the dental clinic check with your general practitioners for any allergies to iodine, food colouring or any other ingredients that may be present in these products. These gels provide a visual aid in assessing plaque biofilm presence and can also show the maturity of the dental plaque.
Plaque disclosing products, also known as disclosants, make plaque clinically visible. Clean surfaces of the teeth do not absorb the disclosant, only rough surfaces. Plaque disclosing gels can be either completed at home or in the dental clinic. Before using these at home or in the dental clinic check with your general practitioners for any allergies to iodine, food colouring or any other ingredients that may be present in these products. These gels provide a visual aid in assessing plaque biofilm presence and can also show the maturity of the dental plaque.
 Disclosing tablets are similar to that of disclosing gels, except that they are placed in the mouth and chewed on for approximately one minute. The remaining tablet or saliva is then spit out. Disclosing gels will show the presence of the plaque, but will often not show the level of maturity of the plaque. Disclosing tablets are often prescribed or given to patients with orthodontic appliances for use before and after tooth brushing to ensure optimal cleaning. These are also helpful educational tools for young children or patients who are struggling to remove dental plaque in certain areas. Disclosing gels and tablets are useful for individuals of all ages in ensuring efficient dental plaque removal.
Disclosing tablets are similar to that of disclosing gels, except that they are placed in the mouth and chewed on for approximately one minute. The remaining tablet or saliva is then spit out. Disclosing gels will show the presence of the plaque, but will often not show the level of maturity of the plaque. Disclosing tablets are often prescribed or given to patients with orthodontic appliances for use before and after tooth brushing to ensure optimal cleaning. These are also helpful educational tools for young children or patients who are struggling to remove dental plaque in certain areas. Disclosing gels and tablets are useful for individuals of all ages in ensuring efficient dental plaque removal.
A Biofilm Primer
{{Authority control Acquired tooth disorders
biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular ...
of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s (mostly bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, but also fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
) that grows on surfaces within the mouth
In animal anatomy, the mouth, also known as the oral cavity, or in Latin cavum oris, is the opening through which many animals take in food and issue vocal sounds. It is also the cavity lying at the upper end of the alimentary canal, bounded on ...
. It is a sticky colorless deposit at first, but when it forms tartar, it is often brown or pale yellow. It is commonly found between the teeth, on the front of teeth, behind teeth, on chewing surfaces, along the gumline
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue linin ...
(supragingival), or below the gumline cervical margins The cervical margin of a tooth is the surface above the junction of the crown of the tooth and the root of the tooth.
See also
* Dental terminology
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. Thi ...
(subgingival). Dental plaque is also known as microbial plaque, oral biofilm, dental biofilm, dental plaque biofilm or bacterial plaque biofilm. Bacterial plaque is one of the major causes for dental decay and gum disease.
Progression and build-up of dental plaque can give rise to tooth decay – the localised destruction of the tissues of the tooth by acid produced from the bacterial degradation of fermentable sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
– and periodontal problems such as gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached ...
and periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cau ...
; hence it is important to disrupt the mass of bacteria and remove it. Plaque control and removal can be achieved with correct daily or twice-daily tooth brushing
Tooth brushing is the act of scrubbing teeth with a toothbrush, usually equipped with toothpaste. Interdental cleaning (with floss or an interdental brush) can be useful with tooth brushing, and together these two activities are the primary me ...
and use of interdental aids such as dental floss
Dental floss is a cord of thin filaments used in interdental cleaning to remove food and dental plaque from between teeth or places a toothbrush has difficulty reaching or is unable to reach. Its regular use as part of oral cleaning is designed ...
and interdental brush
A toothbrush is an oral hygiene tool used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles, atop of which toothpaste can be applied, mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard-to-reach ar ...
es.
Oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out ...
is important as dental biofilms may become acidic causing demineralization of the teeth (also known as dental caries) or harden into dental calculus
In dentistry, calculus or tartar is a form of hardened dental plaque. It is caused by precipitation of minerals from saliva and gingival crevicular fluid (GCF) in plaque on the teeth. This process of precipitation kills the bacterial cells wit ...
(also known as tartar). Calculus cannot be removed through tooth brushing or with interdental aids, but only through professional cleaning.
Plaque formation
Dental plaque is a biofilm that attaches to tooth surfaces, restorations and prosthetic appliances (includingdentures
Dentures (also known as false teeth) are prosthetic devices constructed to replace missing teeth, and are supported by the surrounding soft and hard tissues of the oral cavity. Conventional dentures are removable ( removable partial denture o ...
and bridges
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
) if left undisturbed. Understanding the formation, composition and characteristics of plaque helps in its control. An acquired pellicle is a layer of saliva that is composed of mainly glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
and forms shortly after cleaning of the teeth or exposure of new teeth. Bacteria then attach to the pellicle layer, form micro-colonies, and mature on the tooth, which can result in oral diseases. The following table provides a more detailed (six-step) explanation of biofilm formation:

Components of plaque
Different types of bacteria are normally present in the mouth. These bacteria, as well asleukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
, neutrophils, macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, and lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adap ...
, are part of the normal oral cavity and contribute to the individual's health. Approximately 80–90% of the weight of plaque is water. While 70% of the dry weight is bacteria, the remaining 30% consists of polysaccharides and glycoproteins.
Bacteria
The bulk of themicroorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s that form the biofilm are '' Streptococcus mutans'' and other anaerobes, though the precise composition varies by location in the mouth. Examples of such anaerobes include fusobacterium
''Fusobacterium'' is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-negative, non-sporeforming bacteria belonging to Gracilicutes. Individual cells are slender, rod-shaped bacilli with pointed ends.
Strains of ''Fusobacterium'' cause several human diseases, includi ...
and actinobacteria
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to so ...
. ''S. mutans'' and other anaerobes are the initial colonisers of the tooth surface, and play a major role in the establishment of the early biofilm community. ''Streptococcus mutans'' uses the enzyme glucansucrase
Glucansucrase (also known as glucosyltransferase) is an enzyme in the glycoside hydrolase family GH70 used by lactic acid bacteria to split sucrose and use resulting glucose molecules to build long, sticky biofilm chains. These extracellular ho ...
to convert sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
into a sticky, extracellular, dextran
Dextran is a complex branched glucan ( polysaccharide derived from the condensation of glucose), originally derived from wine. IUPAC defines dextrans as "Branched poly-α-d-glucosides of microbial origin having glycosidic bonds predominantly C-1 ...
-based polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with wa ...
that allows the bacteria to cohere, forming plaque. (Sucrose is the only sugar that bacteria can use to form this sticky polysaccharide). These microorganisms all occur naturally in the oral cavity and are normally harmless. However, failure to remove plaque by regular tooth-brushing allows them to proliferate unchecked and thereby build up in a thick layer, which can by virtue of their ordinary metabolism cause any of various dental diseases for the host. Those microorganisms nearest the tooth surface typically obtain energy by fermenting
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
dietary sucrose; during fermentation they begin to produce acids.
The bacterial equilibrium position varies at different stages of formation. Below is a summary of the bacteria that may be present during the phases of plaque maturation:
* Early biofilm: primarily Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
Gram-positive bacte ...
cocci
* Older biofilm (3–4 days): increased numbers of filaments and fusiforms
* 4–9 days undisturbed: more complex flora with rods, filamentous forms
* 7–14 days: ''Vibrio
''Vibrio'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria, possessing a curved-rod (comma) shape, several species of which can cause foodborne infection, usually associated with eating undercooked seafood. Being highly salt tolerant and unable to survive ...
'' species, spirochete
A spirochaete () or spirochete is a member of the phylum Spirochaetota (), (synonym Spirochaetes) which contains distinctive diderm (double-membrane) gram-negative bacteria, most of which have long, helically coiled (corkscrew-shaped or s ...
s, more Gram-negative organismsWilkins E. ''Clinical Practice of the Dental Hygienist''. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2009
Dental plaque as a biofilm
Dental plaque is considered a biofilm adhered to the tooth surface. It is a meticulously formed microbial community, that is organised to a particular structure and function. Plaque is rich in species, given the fact that about 1000 different bacterial species have been recognised using modern techniques. A clean tooth surface would immediately be colonised by salivary pellicles, which acts as an adhesive. This allows the first bacteria (early colonisers) to attach to the tooth, then colonise and grow. After some growth of early colonisers, the biofilm becomes more compliant to other species of bacteria, known as late colonisers.Early colonisers
* mainly ''Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs ...
'' species (60–90%)
* ''Eikenella
''Eikenella corrodens'' is a Gram-negative facultative anaerobic bacillus that can cause severe invasive disease in humans. It was first identified by M. Eiken in 1958, who called it ''Bacteroides corrodens''. ''E. corrodens'' is a rare pericar ...
'' spp.
* ''Haemophilus
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of t ...
'' spp.
* ''Prevotella
''Prevotella'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria.
''Prevotella'' spp. are members of the oral, vaginal, and gut microbiota and are often recovered from anaerobic infections of the respiratory tract. These infections include aspiration pn ...
'' spp.
* ''Propionibacterium
''Propionibacterium'' is a gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes.
Its members are primarily facultative pa ...
'' spp.
* ''Capnocytophaga
''Capnocytophaga'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. Normally found in the oropharyngeal tract of mammals, they are involved in the pathogenesis of some animal bite wounds and periodontal diseases.
Taxonomy
The term ''Capnocytophaga'' come ...
'' spp.
* ''Veillonella
''Veillonella'' are Gram-negative bacteria (Gram stain pink) anaerobic cocci, unlike most Bacillota, which are Gram-positive bacteria. This bacterium is well known for its lactate fermenting abilities. It is a normal bacterium in the intestine ...
'' spp.
Late colonisers
* ''Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
''Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans'' is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe, nonmotile bacterium that is often found in association with localized aggressive periodontitis, a severe infection of the periodontium. It is also suspected to b ...
''
* ''Prevotella intermedia
''Prevotella intermedia'' (formerly ''Bacteroides intermedius'') is a gram-negative, obligate anaerobic pathogenic bacterium involved in periodontal infections, including gingivitis and periodontitis, and often found in acute necrotizing ulcerat ...
''
* ''Eubacterium
''Eubacterium'' is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Eubacteriaceae. These bacteria are characterised by a rigid cell wall. They may either be motile or nonmotile. If motile, they have a flagellum
A flagellum (; ) is a hair ...
'' spp.
* ''Treponema
''Treponema'' is a genus of spiral-shaped bacteria. The major treponeme species of human pathogens is ''Treponema pallidum'', whose subspecies are responsible for diseases such as syphilis, bejel, and yaws. '' Treponema carateum'' is the cause ...
'' spp.
* ''Porphyromonas gingivalis
''Porphyromonas gingivalis'' belongs to the phylum ''Bacteroidota'' and is a nonmotile, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, anaerobic, pathogenic bacterium. It forms black colonies on blood agar.
It is found in the oral cavity, where it is implicate ...
''
''Fusobacterium nucleatum
''Fusobacterium nucleatum'' is a Gram negative, anaerobic oral bacterium, commensal to the human oral cavity, that plays a role in periodontal disease. This organism is commonly recovered from different monocultured microbial and mixed infection ...
'' is found between the early and late colonisers, linking them together.
Some salivary components are crucial for plaques ecosystem, such as salivary alpha-amylase which plays a role in binding and adhesion. Proline-rich proteins (PRP) and statherins are also involved in the formation of plaque.
Supragingival biofilm
Supragingival biofilm is dental plaque that forms above thegums
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lin ...
, and is the first kind of plaque to form after the brushing of the teeth. It commonly forms in between the teeth, in the pits and grooves of the teeth and along the gums. It is made up of mostly aerobic bacteria, meaning these bacteria need oxygen to survive. If plaque remains on the tooth for a longer period of time, anaerobic bacteria begin to grow in this plaque.
Subgingival biofilm
 Subgingival biofilm is plaque that is located under the gums. It occurs after the formation of the supragingival biofilm by a downward growth of the bacteria from above the gums to below. This plaque is mostly made up of anaerobic bacteria, meaning that these bacteria will only survive if there is no oxygen. As this plaque attaches in a pocket under the gums, they are not exposed to oxygen in the mouth and will therefore thrive if not removed.
The
Subgingival biofilm is plaque that is located under the gums. It occurs after the formation of the supragingival biofilm by a downward growth of the bacteria from above the gums to below. This plaque is mostly made up of anaerobic bacteria, meaning that these bacteria will only survive if there is no oxygen. As this plaque attaches in a pocket under the gums, they are not exposed to oxygen in the mouth and will therefore thrive if not removed.
The extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide stru ...
contains proteins, long-chain polysaccharides and lipids.
The most common reasons for ecosystem disruption are the ecological factors discussed in the environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
section. The bacteria that exhibit the most fit plasticity for the change in environment dominate the given environment. Often, this leads to opportunistic
Opportunism is the practice of taking advantage of circumstances – with little regard for principles or with what the consequences are for others. Opportunist actions are expedient actions guided primarily by self-interested motives. The term ...
pathogens
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
which may cause dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
and periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
. Pathogenic bacteria
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often Probiotic, beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The n ...
that have the potential to cause dental caries flourish in acidic environments; those that have the potential to cause periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
flourish in a slightly alkaline environment.
Antibodies to the oral pathogens ''Campylobacter rectus
''Campylobacter rectus'' is a species of '' Campylobacter''. It is implicated as a pathogen in chronic periodontitis, which can induce bone loss. This motile bacillus is a Gram negative, facultative anaerobe. ''C. rectus'' is associated with hyp ...
'', ''Veillonella parvula
''Veillonella parvula'' is a strictly anaerobic, Gram-negative, coccus-shaped bacterium in the genus '' Veillonella''. It is a normal part of the oral flora but can be associated with diseases such as periodontitis and dental caries as well as va ...
'', ''Prevotella melaninogenica
''Prevotella melaninogenica'' is a species of bacterium in the normal microbiota of the upper respiratory tract. It is an important human pathogen in various anaerobic infections, often mixed with other aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. ''P. melan ...
'' were associated with hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
.
Environment
Unlike other parts of the body, tooth surfaces are uniquely hard and non shedding. Therefore, the warm and moist environment of the mouth and the presence of teeth, makes a good environment for growth and development of dental plaque. The main ecological factors that contribute to plaque formation are pH,saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
, temperature and redox reaction
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
s. The normal pH range of saliva is between 6 and 7 and plaque biofilm is known to flourish in a pH between 6.7 and 8.3. This indicates that the natural environment of the mouth provided by saliva is ideal for the growth of bacteria in the dental plaque. Saliva acts as a buffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* ...
, which helps to maintain the pH in the mouth between 6 and 7. In addition to acting as a buffer, saliva and gingival crevicular fluid contain primary nutrients including amino acids, proteins and glycoproteins. This feeds the bacteria involved in plaque formation. The host diet plays only a minor role in providing nutrients for the resident microflora. The normal temperature of the mouth ranges between 35 and 36 °C, and a two-degree (°C) change has been shown to drastically shift the dominant species in the plaque. Redox reactions
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a d ...
are carried out by aerobic bacteria
Aerobic means "requiring air," in which "air" usually means oxygen.
Aerobic may also refer to
* Aerobic exercise, prolonged exercise of moderate intensity
* Aerobics, a form of aerobic exercise
* Aerobic respiration, the aerobic process of cell ...
. This keeps the oxygen levels in the mouth at a semi-stable homeostatic condition, which allows the bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
to survive.
Consequences of plaque build-up
Gingivitis

Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a non-destructive disease that causes inflammation of the gums. The most common form of gingivitis, and the most common form of periodontal disease overall, is in response to bacterial biofilms (also called plaque) that is attached ...
is an inflammatory lesion, mediated by host-parasite interactions that remains localised to the gingival tissue, it is a common result of plaque build-up around the gingival tissues. The bacteria found in the biofilm elicit a host response resulting in localized inflammation of the tissue. This is characterized by the cardinal signs of inflammation including a red, puffy appearance of the gums and bleeding due to brushing or flossing.
Gingivitis due to plaque can be reversible by removal of the plaque. However, if left for an extended period of time, the inflammation may begin to affect the supporting tissues, in a progression referred to as periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cau ...
. The gingivitis response is a protective mechanism, averting periodontitis in many cases.
Periodontitis
 Periodontitis is an infection of the gums which leads to bone destruction around the teeth in the jaw. Periodontitis occurs after gingivitis has been established, but not all individuals who have gingivitis will get periodontitis. Plaque accumulation is vital in the progression of periodontitis as the
Periodontitis is an infection of the gums which leads to bone destruction around the teeth in the jaw. Periodontitis occurs after gingivitis has been established, but not all individuals who have gingivitis will get periodontitis. Plaque accumulation is vital in the progression of periodontitis as the bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
in plaque release enzymes which attack the bone and cause it to break down, and at the same time osteoclasts
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated prote ...
in the bone break down the bone as a way to prevent further infection. This can be treated with strict oral hygiene such as tooth brushing and cleaning in between the teeth as well as surgical debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
In p ...
completed by a dental professional.
Diseases linked to periodontitis
Accumulated bacteria, due to the onset of periodontitis from dental plaque, may gain access to distant sites in the body through the circulatory and respiratory system, potentially contributing to various systematic diseases and conditions. Due to the infectious nature of bacteria hosted within the oral cavity, bacteria produced cavity can spread within the system of the human body and causes adverse health conditions. Bacteria access comes from theulcerated epithelium
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing o ...
of the periodontal pocket that results from accumulation of infection within the gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lini ...
. Conditions and diseases can include:
*Atheroma
An atheroma, or atheromatous plaque, is an abnormal and reversible accumulation of material in the inner layer of an arterial wall.
The material consists of mostly macrophage cells, or debris, containing lipids, calcium and a variable amount o ...
sCardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, h ...
*Respiratory disease
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathology, pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in Breathing, air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the t ...
*Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ap ...
Caries

Dental caries
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
is an infectious disease caused primarily by ''Streptococcus mutans'', characterized by acid demineralization of the enamel, which can progress to further breakdown of the more organic, inner dental tissue (dentin
Dentin () (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) ( la, substantia eburnea) is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by ena ...
). The bacterial community would mainly consist of acidogenic and acid-tolerating species (e.g. ''Mutans streptococci'' and ''lactobacilli''), while other species with relevant characteristics may also be involved.
Everybody is susceptible to caries but the probability of development depends on the patient’s individual disease indicators, risk factors, and preventive factors. Factors that are considered high-risk for developing carious lesions on the teeth include:
* Low fluoride exposure
* Time, length, and frequency of sugar consumption
* Quality of tooth cleaning
* Fluctuations in salivary flow rates and composition
* Behavior of the individual
* Quality and composition of biofilms
Organic acids released from dental plaque lead to demineralization of the adjacent tooth surface, and consequently to dental caries. Saliva
Saliva (commonly referred to as spit) is an extracellular fluid produced and secreted by salivary glands in the mouth. In humans, saliva is around 99% water, plus electrolytes, mucus, white blood cells, epithelial cells (from which DNA can be ...
is also unable to penetrate the build-up of plaque and thus cannot act to neutralize the acid produced by the bacteria and remineralize the tooth surface.
Detection of plaque build-up
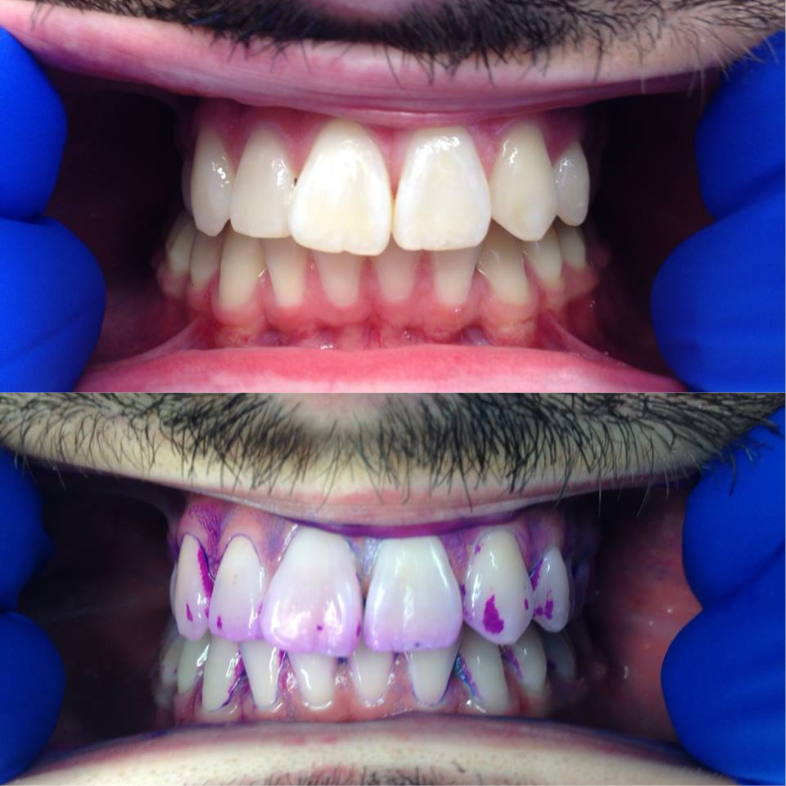
There are two main methods of detecting dental plaque in the oral cavity: through the application of a disclosing gel or tablet, and/or visually through observation. Plaque detection is usually detected clinically by plaque disclosing agents. Disclosing agents contain dye which turns bright red to indicate plaque build-up. It is important for an individual to be aware of what to look for when doing a self-assessment for dental plaque. It is important to be aware that everyone has dental plaque, however, the severity of the build-up and the consequences of not removing the plaque can vary.Plaque disclosing gel
 Plaque disclosing products, also known as disclosants, make plaque clinically visible. Clean surfaces of the teeth do not absorb the disclosant, only rough surfaces. Plaque disclosing gels can be either completed at home or in the dental clinic. Before using these at home or in the dental clinic check with your general practitioners for any allergies to iodine, food colouring or any other ingredients that may be present in these products. These gels provide a visual aid in assessing plaque biofilm presence and can also show the maturity of the dental plaque.
Plaque disclosing products, also known as disclosants, make plaque clinically visible. Clean surfaces of the teeth do not absorb the disclosant, only rough surfaces. Plaque disclosing gels can be either completed at home or in the dental clinic. Before using these at home or in the dental clinic check with your general practitioners for any allergies to iodine, food colouring or any other ingredients that may be present in these products. These gels provide a visual aid in assessing plaque biofilm presence and can also show the maturity of the dental plaque.
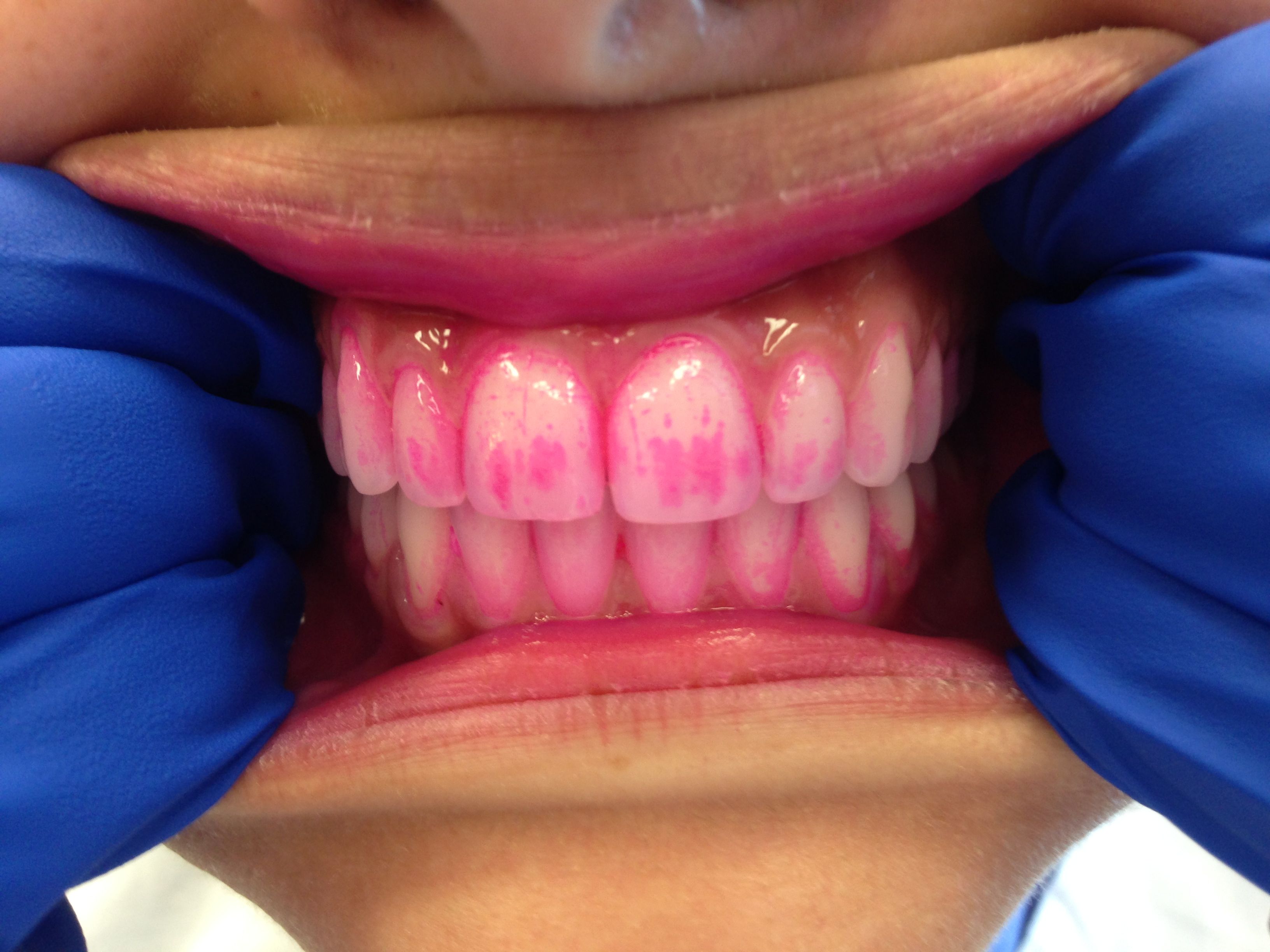
Disclosing tablets
 Disclosing tablets are similar to that of disclosing gels, except that they are placed in the mouth and chewed on for approximately one minute. The remaining tablet or saliva is then spit out. Disclosing gels will show the presence of the plaque, but will often not show the level of maturity of the plaque. Disclosing tablets are often prescribed or given to patients with orthodontic appliances for use before and after tooth brushing to ensure optimal cleaning. These are also helpful educational tools for young children or patients who are struggling to remove dental plaque in certain areas. Disclosing gels and tablets are useful for individuals of all ages in ensuring efficient dental plaque removal.
Disclosing tablets are similar to that of disclosing gels, except that they are placed in the mouth and chewed on for approximately one minute. The remaining tablet or saliva is then spit out. Disclosing gels will show the presence of the plaque, but will often not show the level of maturity of the plaque. Disclosing tablets are often prescribed or given to patients with orthodontic appliances for use before and after tooth brushing to ensure optimal cleaning. These are also helpful educational tools for young children or patients who are struggling to remove dental plaque in certain areas. Disclosing gels and tablets are useful for individuals of all ages in ensuring efficient dental plaque removal.
Visual or tactile detection
Dental biofilm begins to form on the tooth only minutes after brushing. It can be difficult to see dental plaque on the hard tissue surfaces, however it can be felt as a rough surface. It is often felt as a thick, fur-like deposit that may present as a yellow, tan or brown stain. These deposits are commonly found on teeth or dental appliances such as orthodontic brackets. The most common way dental plaque is assessed is through dental assessment in the dental clinic where dental instruments are able to scrape up some plaque. The most common areas where patients find plaque are between the teeth and along thecervical margins The cervical margin of a tooth is the surface above the junction of the crown of the tooth and the root of the tooth.
See also
* Dental terminology
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. Thi ...
.
Plaque in dogs and cats
Dental plaque is also extremely common in domestic animals such as dogs and cats. However, the bacteria associated with canine and feline plaque appear to be different from those of humans. If untreated it can lead to more severe gum disease such as periodontitis; hence veterinarians often recommend oral healthcare products for affected pets.See also
*Flossing
Dental floss is a cord of thin filaments used in interdental cleaning to remove food and dental plaque from between teeth or places a toothbrush has difficulty reaching or is unable to reach. Its regular use as part of oral cleaning is designed ...
*Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health.
Structure
The gums are part of the soft tissue lini ...
*Dental disease
Tooth pathology is any condition of the teeth that can be congenital or acquired. Sometimes a congenital tooth diseases are called ''tooth abnormalities''. These are among the most common diseases in humans The prevention, diagnosis, treatment and ...
*Oral hygiene
Oral hygiene is the practice of keeping one's mouth clean and free of disease and other problems (e.g. bad breath) by regular brushing of the teeth (dental hygiene) and cleaning between the teeth. It is important that oral hygiene be carried out ...
*Oral microbiology
Oral microbiology is the study of the microorganisms (microbiota) of the oral cavity and their interactions between oral microorganisms or with the host. The environment present in the human mouth is suited to the growth of characteristic micro ...
References
External links
A Biofilm Primer
{{Authority control Acquired tooth disorders